Our first blog in this series, on counter-unmanned aircraft systems (C-UAS) solutions, looked at some reasons that such systems are necessary. This blog examines some of the data sources that can be used within C-UAS solutions.
Data sources for threat anticipation
To effectively anticipate and respond to threats posed by drones, a geospatial command and control (C2) system relies on various data sources that provide crucial information about the airspace. Some key data sources utilised within the C2 system are radio frequency sensors, radar sensors and video data.
Radio frequency (RF) sensors
RF sensors serve as a fundamental data source in the geospatial C2 system. These sensors analyse the electromagnetic spectrum to detect and classify drone signals. By monitoring the RF spectrum, the C2 system can identify drones based on their unique radio frequency signatures and discern their communication patterns. The data from RF sensors provides insights into the presence, behaviour and intent of drones, contributing to early threat detection and assessment.
Radar sensors
Radar sensors play a vital role in the geospatial C2 system by providing comprehensive airspace surveillance. These sensors emit radio waves and analyse the echoes reflected back from objects, including drones. The radar sensors usually are equipped with enough intelligence to determine whether the object detected is a suspected drone or another object (a bird, for example). Based on this attribute, the C2 system is capable of making sense out of all the received data. By accurately determining the position, velocity and altitude of drones, radar sensors enable real-time monitoring, tracking and situational awareness. Radar data enhances the C2 system’s ability to detect, track and respond to drone threats effectively.
Video data
Video data, acquired from drones or external surveillance systems, offers valuable visual information for threat identification and tracking. Real-time video feeds captured by onboard drone cameras or external cameras provide operators within the C2 system with a visual understanding of the airspace. Video analytics techniques can be employed to automatically detect suspicious activities or unauthorized drone operations, enhancing the system’s situational awareness and response capabilities.
Core capabilities of the geospatial C2 system
The geospatial C2 system encompasses a range of capabilities that work together to anticipate and mitigate drone threats. In this section, we will explore the core capabilities of the C2 system.
Detection and identification
The C2 system integrates data from various sources to detect and identify drones. By analysing RF signatures, radar returns and video feeds, the system can identify the presence and characteristics of drones, distinguishing them from other objects in the airspace.
Tracking and monitoring
Once drones are detected and identified, the C2 system employs tracking algorithms to monitor their movements accurately. This capability enables operators to maintain real-time situational awareness, track the positions of drones and predict their trajectories.
Threat assessment and classification
The C2 system utilizes advanced algorithms and analytics to assess the nature and severity of drone threats. By analysing data from multiple sources, including RF signals, radar returns and video footage, the system can classify drones based on their behaviour and intent, and give a potential risk level. This will result in drones classed as known/unknown, threat/friendly, etc.
Decision support and response
Based on the threat assessment, the C2 system provides decision support tools to operators, assisting them in determining the appropriate response strategies. This includes generating alerts, providing visualizations and recommending countermeasures to mitigate the identified threats effectively.
Integration of countermeasures
The geospatial C2 system facilitates the integration and coordination of countermeasures to neutralise drone threats. This involves deploying counter-UAS technologies, activating appropriate response protocols and engaging with relevant security forces to ensure a swift and effective response.
By utilising the data from RF sensors, radar sensors and video sources, and leveraging the core capabilities of the geospatial C2 system, organisations can anticipate and respond to drone threats in a proactive and coordinated manner.
Enhancing decision-making with 3D visualisations
In the field of geospatial C2 systems, 3D visualisation has emerged as a powerful tool that enhances the decision-making process. 3D visualisation leverages advanced computer graphics technologies to represent dynamic and static geospatial data in a real-world view. By transforming complex data into visual representations, the C2 system provides operators with an intuitive and immersive understanding of the operational environment. This visual context enhances situational awareness and facilitates quicker, more effective decision-making.
Enhanced situational awareness
3D visualisation enables operators to visualise airspace, terrain, structures and objects in a realistic and intuitive manner. By overlaying drone positions, flight paths and relevant geospatial data onto a 3D model, operators gain a comprehensive understanding of the operational context. This enhanced situational awareness allows for better assessment of threats, identification of vulnerabilities and evaluation of potential impact scenarios.
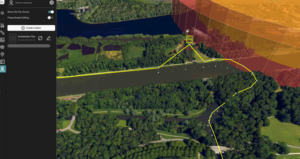
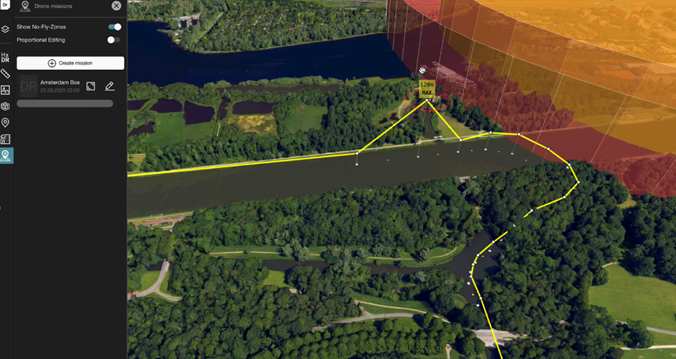
UAV flightpath and restricted area (no fly zone) in 3D (developed in Hexagon’s LuciadRIA).
Spatial relationships and proximity analysis
With 3D visualisation, operators can accurately perceive spatial relationships between drones, critical assets and infrastructure. By visualising proximity and potential collision risks, operators can assess the severity of threats and prioritize response actions accordingly. This capability enhances the ability to identify potential vulnerabilities and take effective countermeasures.
Real-time tracking and playback
The interactive nature of 3D visualisation enables operators to track drones in real-time and replay historical data. This functionality aids in reconstructing past events, analysing patterns of behaviour and identifying potential trends or anomalies. By visualising the movement of drones over time, operators can identify patterns and make intelligence-driven decisions.
Simulation and what-if analysis
3D visualisation facilitates simulation and what-if analysis, allowing operators to explore various scenarios and evaluate the potential outcomes of different decisions. By manipulating variables such as drone trajectories, response strategies and environmental factors, operators can assess the effectiveness of different courses of action before implementing them in real time. This capability empowers operators to make more informed and proactive decisions.
Collaboration and communication
3D visualisation promotes effective collaboration and communication among the C2 system operators and stakeholders. By providing a shared visual representation of the operational environment, operators can easily communicate complex information, coordinate response efforts and gain consensus on the best course of action. This improves coordination between different teams and agencies involved in the C2 system.
By incorporating 3D visualisation capabilities, geospatial C2 systems empower operators to make more informed decisions, respond promptly to threats and effectively coordinate countermeasures. The enhanced situational awareness, spatial analysis, real-time tracking, simulation capabilities and improved collaboration offered by 3D visualisation contribute to more efficient and effective threat response.
Our third blog in this series will look at utilising modern techniques in artificial intelligence and machine learning for C-UAS systems. In the meantime, check out this article on how countering UAS underscores the need for modern C6ISR capabilities.